Hello, today I want to talk to you about a condition that often goes unnoticed but can have a significant impact on your health – zinc deficiency. Zinc is a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, from supporting the immune system to wound healing and even the senses of taste and smell.
But how do you know if you have a zinc deficiency? What are the signs of zinc deficiency? Well, there are certain signs and symptoms that you can look out for. These include skin changes resembling eczema, hair loss, frequent infections, delayed wound healing, loss of taste and smell, and even diarrhea. It’s essential to recognize these symptoms so that you can take the necessary steps to address the deficiency and prevent further complications.
There are several reasons why someone may develop a zinc deficiency. It can be caused by problems with zinc absorption, inadequate zinc intake, or certain medical conditions. Understanding the underlying causes can help you identify the root issue and find an appropriate treatment plan.
Treating zinc deficiency usually involves taking zinc supplements and consuming foods that are high in zinc. By ensuring adequate zinc intake, you can reap the numerous health benefits and improve your overall well-being.
Signs of Zinc Deficiency
- Zinc deficiency can lead to various symptoms, including skin changes, hair loss, and frequent infections.
- Factors such as inadequate zinc intake and problems with absorption can cause a zinc deficiency.
- Treatment often involves taking zinc supplements and incorporating zinc-rich foods into your diet.
- Recognizing the symptoms of zinc deficiency is crucial for early intervention and prevention of further complications.
- Consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for accurate diagnosis and recommendations for zinc supplementation.
Understanding Zinc and its Importance in the Body
Zinc is a vital mineral that plays a crucial role in several important bodily functions. It is essential for supporting a healthy immune system, promoting wound healing, aiding in blood clotting, maintaining proper thyroid function, and ensuring the senses of taste and smell are functioning optimally.
Furthermore, zinc is particularly important during growth and development stages. It supports normal growth and development during pregnancy, childhood, and adolescence, contributing to overall health and well-being.
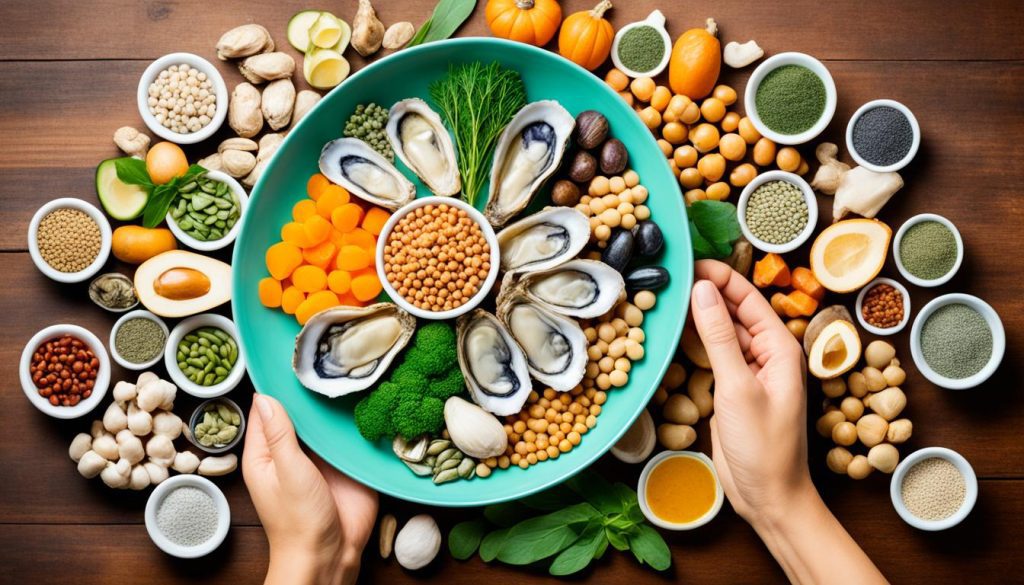
To ensure an adequate intake of zinc, it is important to include zinc-rich foods in your diet. Some excellent sources of zinc include dairy products, poultry, meat, seafood, cereals, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
Consuming zinc-rich foods provides numerous health benefits. It supports a strong immune system, which can help defend against illnesses and infections. Additionally, zinc plays a crucial role in the wound healing process, promoting the formation of new tissue and reducing the risk of infection.
Zinc is also involved in blood clotting, ensuring that wounds close properly. It supports proper thyroid function, which is essential for regulating metabolism and overall energy levels.
Furthermore, zinc is closely linked to the senses of taste and smell. Adequate zinc levels are necessary for experiencing these senses fully and accurately.
Finally, during pregnancy, childhood, and adolescence, zinc is particularly important for growth and development. It helps support the development of tissues, bones, and organs, ensuring healthy growth and optimal function.
By including zinc-rich foods in your diet, you can reap the many benefits of this essential mineral. Whether you are looking to support your immune system, promote wound healing, enhance taste and smell, or ensure proper growth and development, zinc is a key player in maintaining overall health and well-being.
Recognizing the Symptoms of Zinc Deficiency
Zinc deficiency can manifest in various symptoms that can significantly impact overall health and well-being. By recognizing these signs, it becomes easier to identify a potential zinc deficiency and prompt appropriate intervention.
Skin Changes:
Zinc deficiency can cause skin changes resembling eczema. These changes may include dryness, redness, inflammation, and rough patches on the skin.
Hair Loss:
Another symptom of zinc deficiency is hair loss. This can manifest as thinning hair, hair breakage, or even bald patches.
Eye Problems:
Inadequate zinc levels can also lead to eye problems such as night blindness or poor vision in low-light conditions.
Frequent Infections:
Individuals with zinc deficiency may experience more frequent infections, as zinc plays a crucial role in supporting a healthy immune system.
Slow Wound Healing:
Delayed wound healing is another common symptom of zinc deficiency. It may take longer for wounds, cuts, or sores to heal properly.
Loss of Taste and Smell:
Zinc deficiency can affect the senses of taste and smell, leading to a decreased ability to perceive or distinguish flavors and scents.
Diarrhea:
Individuals deficient in zinc may experience frequent episodes of diarrhea. This can contribute to electrolyte imbalances and dehydration.
Slow Growth in Children:
Zinc plays a crucial role in growth and development, especially in children. Slow growth or delayed milestones may indicate zinc deficiency.
Brain Fog:
Zinc deficiency can also affect cognitive function, resulting in difficulties with concentration, memory, and mental clarity.
Drops in Blood Sugar:
Some individuals with zinc deficiency may experience drops in blood sugar levels, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, and lightheadedness.

Causes of Zinc Deficiency
Zinc deficiency can occur due to a variety of factors that disrupt the body’s zinc levels. Understanding these causes is essential in addressing the root issues and preventing further deficiencies. The following are some common causes of zinc deficiency:
- Problems Absorbing Zinc: Certain conditions or diseases can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb zinc from the diet, leading to inadequate levels in the body.
- Inadequate Zinc Intake: Not consuming enough zinc-rich foods can result in insufficient zinc levels and eventually lead to deficiency.
- Gastrointestinal Diseases: Some gastrointestinal diseases, such as Crohn’s disease and celiac disease, can impair nutrient absorption, including zinc.
- Medication-Induced Zinc Loss: Certain medications, such as diuretics and some antibiotics, can increase the loss of zinc through urine, depleting the body’s zinc stores.
- Low Zinc Levels in Breastmilk: Breastmilk naturally contains zinc, but in some cases, the levels may be insufficient to meet the nutritional needs of the infant, leading to zinc deficiency.
- Newborn Zinc Deficiency: Rarely, newborns may be born with low zinc levels, putting them at risk of deficiency from birth.
Identifying the causes of zinc deficiency is key to addressing the underlying issues and implementing appropriate interventions. By understanding these factors, individuals can take steps to prevent and correct zinc deficiency, ensuring optimal health and well-being.
Diagnosing and Treating Zinc Deficiency
When it comes to diagnosing zinc deficiency, blood tests are often utilized. However, it’s important to note that these tests may not always be reliable for detecting mild deficiencies. In some cases, individuals with mild zinc deficiency may display normal blood test results, making it challenging to identify the deficiency accurately.
Once diagnosed, the next step in treating zinc deficiency is often the prescription of zinc supplements. These supplements can provide the body with the necessary amount of zinc it needs to address the deficiency effectively. One of the significant advantages of zinc supplementation is the rapid improvement in symptoms that individuals may experience.
However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate zinc dosage for supplementation. Excessive intake of zinc can have adverse effects and lead to toxicity. A healthcare professional can assess an individual’s specific needs and recommend the optimal dosage for safe and effective treatment.
To prevent zinc deficiency, incorporating zinc-rich foods into the diet is essential. Additionally, there are zinc-fortified supplements available in the market that can help maintain optimal zinc levels. These supplements provide an extra boost of zinc and serve as a preventive measure against deficiencies. However, it’s important to be aware that certain factors can interfere with zinc absorption, such as the presence of certain dietary compounds. Consulting with a healthcare professional can help address any potential interference and ensure the prevention of zinc deficiency.

- Blood tests may not always accurately detect mild zinc deficiencies.
- Zinc supplements are often recommended to treat zinc deficiency and can lead to rapid symptom improvement.
- Consult with a healthcare professional for the appropriate zinc dosage to avoid excessive intake.
- Incorporating zinc-rich foods and utilizing zinc-fortified supplements can help prevent zinc deficiency.
- A healthcare professional can address any interference with zinc absorption to ensure effective prevention.
Who is at Risk for Zinc Deficiency?
Certain individuals are at a higher risk of zinc deficiency.
- Pregnant women: Pregnant women require increased zinc intake for proper fetal development. It is crucial for their health and the health of their baby.
- Vegetarians: Vegetarians may be at risk of zinc deficiency due to their limited food sources that are rich in zinc, such as meat and seafood.
- Gastrointestinal diseases: People with gastrointestinal diseases that affect nutrient absorption, such as Crohn’s disease or celiac disease, are more prone to zinc deficiency.
- Infants exclusively breastfed beyond six months: Infants who are exclusively breastfed beyond six months may experience zinc deficiency due to the low zinc content in breastmilk as their nutritional needs increase.
Recognizing these risk factors is important as it helps identify individuals who may require additional attention and intervention to prevent or address zinc deficiency.
Conclusion
Zinc deficiency can have significant effects on overall health and well-being. Individuals experiencing symptoms such as skin changes, hair loss, weakened immune system, delayed wound healing, and impaired senses of taste and smell should be aware of the possibility of zinc deficiency. Factors such as problems with absorption, inadequate zinc intake, and certain medical conditions can contribute to this deficiency.
Diagnosing zinc deficiency involves blood tests, although they may not always be reliable, especially for mild deficiencies. Treatment typically involves the use of zinc supplements, which have shown to lead to significant improvements in symptoms. It is crucial for individuals to consult with healthcare professionals to determine appropriate zinc dosages and avoid excessive intake.
In addition to supplementation, addressing zinc deficiency can also be achieved through dietary changes. Consuming zinc-rich foods such as dairy products, poultry, meat, seafood, cereals, legumes, nuts, and seeds can help maintain optimal zinc levels and prevent deficiencies. By recognizing the signs of zinc deficiency and taking proactive actions, individuals can effectively manage and prevent zinc deficiency, promoting their overall health and well-being.
FAQ
What are the signs of zinc deficiency?
The signs of zinc deficiency include skin changes resembling eczema, hair loss, frequent infections, delayed wound healing, loss of taste and smell, and diarrhea.
What are the effects of zinc deficiency?
Zinc deficiency can result in weakened immune system, impaired wound healing, decreased senses of taste and smell, and other health complications.
How is zinc deficiency treated?
Zinc deficiency is typically treated by taking zinc supplements and consuming foods that are high in zinc.
What causes zinc deficiency?
Zinc deficiency can be caused by problems with zinc absorption, inadequate zinc intake, certain medical conditions, and other factors.
How is zinc deficiency diagnosed?
Zinc deficiency can be diagnosed through blood tests, although they may not be reliable for mild deficiencies.
Are there any complications associated with zinc deficiency?
Yes, zinc deficiency can lead to various complications such as skin problems, hair loss, and weakened immune system.
Who is at risk for zinc deficiency?
Pregnant women, vegetarians, individuals with gastrointestinal diseases, and infants exclusively breastfed beyond six months are at a higher risk of zinc deficiency.
What are the benefits of zinc supplements?
Zinc supplements can help improve symptoms of zinc deficiency and maintain optimal zinc levels in the body.
How can I prevent zinc deficiency?
To prevent zinc deficiency, you can consume zinc-rich foods and follow healthcare professional recommendations for supplementation.