Periodontal disease affects approximately 70 percent of adults in the US, making it a common oral health concern. One of the main worries for those with periodontal disease is the potential loss of teeth. Gingivitis, the early stage of periodontal disease, can progress to periodontitis if left untreated, leading to tooth loss.
But here’s the good news – with proper oral care and maintenance, it is possible to preserve your teeth, even with periodontal disease. In this article, we will explore the link between periodontal disease and tooth loss, the symptoms to watch for, and strategies to maintain your dental health.
By understanding how to effectively manage periodontal disease, you can keep your teeth and enjoy a healthy smile for years to come. Let’s dive in!
Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
When it comes to maintaining your teeth with gum disease, recognizing the symptoms of periodontal disease is crucial. The early stage of gum disease, known as gingivitis, can manifest as bleeding gums, tenderness, redness, and gum recession. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which can cause more severe symptoms such as tooth loss, painful chewing, and further separation of gums from teeth.
Proper dental care is essential for maintaining teeth with gum disease. Regularly brushing your teeth with a soft-bristled toothbrush and flossing daily can help remove plaque and prevent the progression of gum disease. Additionally, scheduling regular dental cleanings is important for removing tartar buildup and monitoring the health of your gums.
The Role of Oral Hygiene in Preserving Teeth with Periodontal Disease
Oral hygiene plays a crucial role in preserving teeth when dealing with periodontal disease. Alongside regular brushing and flossing, using an antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce the buildup of harmful bacteria that contribute to gum disease. It’s also important to maintain a healthy diet, limit sugary foods and drinks, and avoid smoking, as these factors can worsen gum disease.
By staying proactive in your oral care routine and seeking professional dental treatment, you can maintain your teeth even with periodontal disease. Remember to schedule regular check-ups with your dentist and communicate any concerns or changes in your oral health. With proper dental care and maintenance, it is possible to preserve your teeth and minimize the impact of periodontal disease on your oral health.
How Long Can Teeth Last with Periodontal Disease?
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, can have long-term effects on the health of your teeth. It is a common condition that affects many adults, with symptoms ranging from gum inflammation and bleeding to more severe issues like tooth loss. However, with proper care and management, it is possible to preserve your teeth even with periodontal disease.
The Long-Term Effects of Periodontal Disease on Teeth
A study conducted in 1978 found that approximately 31% of teeth in people with periodontal disease were lost over a 22-year examination period. However, it is important to note that half of the participants in the study did not experience any tooth loss at all. Another study from 2003 showed that only about 50% of patients with periodontal disease experienced tooth loss over a 12-year period. These findings suggest that with proper oral care and treatment, it is possible to maintain your teeth even in the presence of periodontal disease.
Tooth Survival with Periodontal Disease
While periodontal disease can pose a risk to your oral health, it does not necessarily mean that you will lose all of your teeth. By adopting a comprehensive approach to dental care, including regular brushing and flossing, routine dental check-ups, and professional cleanings, you can increase the likelihood of tooth survival. Additionally, seeking timely treatment for periodontal disease, such as scaling and root planing, can help manage the condition and preserve your teeth for the long term.
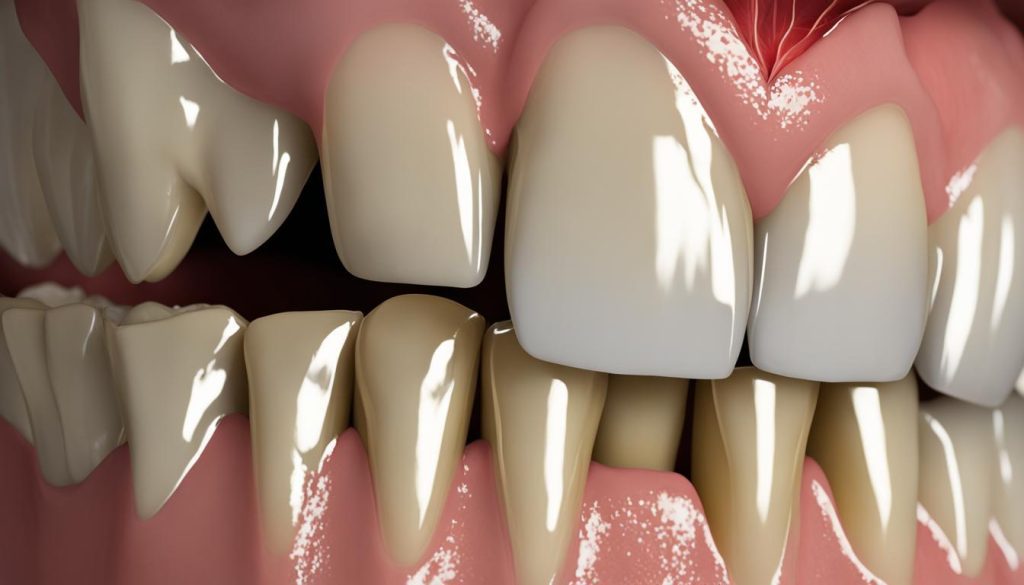
Risk Factors for Periodontal Disease
When it comes to periodontal disease, understanding the risk factors can help in preventing tooth loss and devising strategies for keeping teeth in the presence of gum disease. Several factors contribute to the development and progression of periodontal disease, making it crucial to manage them effectively. By addressing these risk factors and practicing good oral hygiene, it is possible to prevent tooth loss from periodontal disease and retain your teeth.
Managing Stress and Systemic Diseases
Stress and systemic diseases such as diabetes can increase the risk of periodontal disease and tooth loss. It is important to find effective ways to manage stress, such as engaging in stress-relieving activities or seeking professional help if needed. Additionally, controlling diabetes through proper medication and lifestyle choices can contribute to better gum health and tooth retention.
Quitting Smoking and Chewing Tobacco
Smoking and chewing tobacco not only stains teeth but also weaken oral tissues, making them more susceptible to periodontal disease. Quitting these habits can significantly reduce the risk of gum disease and increase the chances of keeping your teeth in the long run. There are various resources available to help individuals quit smoking or chewing tobacco, ranging from counseling to nicotine replacement therapies.
Maintaining Good Oral Hygiene
Proper oral hygiene practices play a crucial role in preventing tooth loss from periodontal disease. Regular brushing with a soft-bristled toothbrush, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash can help remove plaque and bacteria, reducing the likelihood of developing gum disease. Incorporate these habits into your daily routine and visit your dentist regularly for professional cleanings to maintain optimal oral health and tooth retention.
Dental Care for Teeth with Periodontal Disease
When it comes to periodontal disease, proper dental care is crucial in preventing tooth loss and maintaining your teeth. While periodontal disease cannot be cured, it can be managed and its progression can be slowed down with the right strategies. One of the most important steps is to follow a consistent dental care regimen that focuses on maintaining oral hygiene.
This includes brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Be sure to brush along the gumline and the surfaces of your teeth. Don’t forget to floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline.
In addition to regular brushing and flossing, it is essential to schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings. Your dentist can remove plaque and tartar buildup that you may have missed during your oral care routine. They can also evaluate the health of your gums and provide necessary treatments or recommendations to help reverse periodontal disease.
Preventing Tooth Loss from Periodontal Disease
Alongside maintaining good oral hygiene practices, adopting a healthy diet can also contribute to preserving your teeth. Avoiding sugary foods and drinks, as well as limiting your intake of acidic foods and beverages, can help prevent further damage to your teeth and gums. Additionally, quitting smoking and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption can significantly reduce your risk of tooth loss from periodontal disease.
By committing to a comprehensive dental care routine, managing risk factors, and seeking professional treatment, you can take proactive steps to preserve your teeth and prevent tooth loss in the presence of periodontal disease.
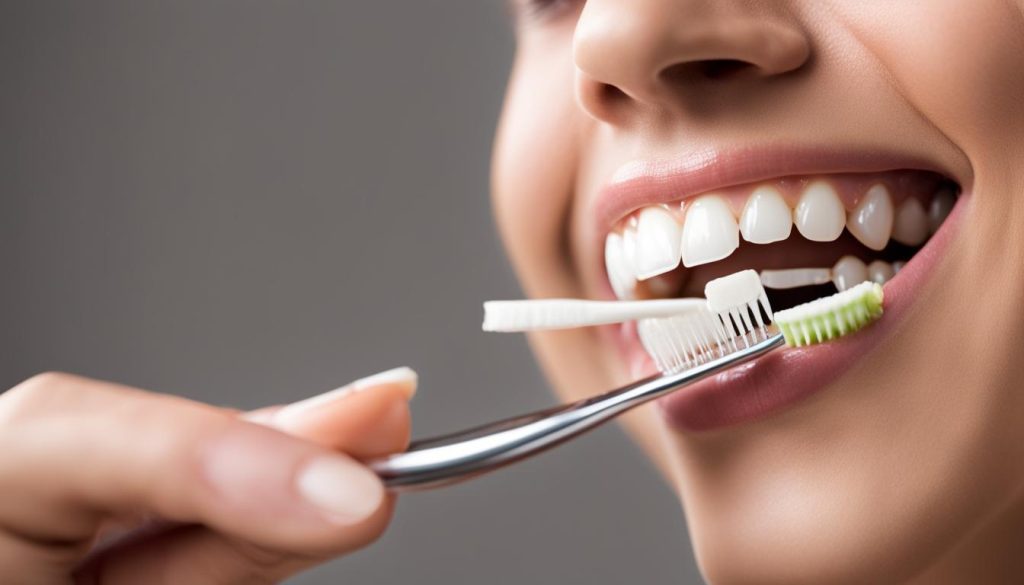
Maintaining Dental Health
When it comes to preserving teeth with periodontal disease, dental care plays a crucial role. By following a consistent dental care regimen, individuals can effectively manage the disease and maintain their oral health. Here are some key practices to incorporate into your routine:
1. Brushing and Flossing:
Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Be sure to clean the gumline and all tooth surfaces. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline. These habits help prevent the build-up of bacteria and reduce the risk of gum disease progression.
2. Regular Dental Check-ups:
Make it a priority to visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings. Professional cleanings remove plaque and tartar buildup, which cannot be removed by brushing and flossing alone. These appointments also allow your dentist to monitor your oral health and detect any potential issues early on.
3. Healthy Diet and Lifestyle:
Eating a balanced diet that is rich in essential nutrients, such as calcium and vitamin C, can benefit your dental health. Limit sugary snacks and beverages, as they can contribute to tooth decay. Additionally, avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, as these habits can worsen gum disease and affect overall oral health.
By incorporating these practices into your daily routine, you can effectively maintain your dental health and reduce the impact of periodontal disease on your teeth. Remember, proper dental care is essential for preserving teeth and improving overall oral health.
The Link Between Periodontal Disease and Overall Health
Research has established a significant connection between periodontal disease and overall health. It is not just a problem limited to the gums and teeth; it can have implications for the entire body. Studies have revealed associations between periodontal disease and various systemic conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, respiratory disease, and certain types of cancer.
One reason for this link is the ability of the bacteria from periodontal disease to enter the bloodstream and spread throughout the body. This can lead to inflammation and immune system responses that affect different organs and tissues. For example, the systemic inflammation caused by periodontal disease can contribute to the development or progression of conditions like diabetes and cardiovascular disease.
Addressing periodontal disease is not only crucial for preserving teeth but also for improving overall health. By preventing and treating periodontal disease, individuals can reduce the risk of developing or exacerbating systemic health conditions. This emphasizes the importance of regular dental check-ups, cleanings, and following the advice and treatment recommendations of dental professionals.
The Impact of Periodontal Disease on Overall Health
Periodontal disease can have far-reaching consequences for overall health. Studies have shown that individuals with periodontal disease have a higher likelihood of experiencing complications in other areas of their health. For example, the chronic inflammation associated with periodontal disease can negatively affect the body’s immune response, making it harder to fight off infections and increasing the risk of respiratory issues.
Moreover, periodontal disease has been linked to an increased risk of developing systemic conditions such as cardiovascular disease. The bacteria and toxins from gum infections can enter the bloodstream, triggering inflammation and potentially contributing to the formation of plaque in the arteries. This can lead to a higher risk of heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular events.
In addition to cardiovascular disease, periodontal disease has been associated with an increased risk of diabetes, certain types of cancer, and adverse pregnancy outcomes. The bacteria and inflammation associated with gum disease can impact insulin sensitivity, potentially exacerbating diabetes. Furthermore, research suggests that the chronic inflammation from periodontal disease may play a role in the development or progression of certain cancers. Pregnant individuals with untreated gum disease are also at a higher risk of preterm birth and low birth weight.
In conclusion, the impact of periodontal disease goes beyond oral health. It can influence various aspects of systemic health, including the immune system, cardiovascular system, and metabolic health. By prioritizing oral care, seeking timely treatment, and maintaining regular dental check-ups, individuals can not only preserve their teeth but also contribute to better overall health.
Conclusion
After exploring the various aspects of periodontal disease and its impact on teeth, it is evident that with proper dental care and maintenance, it is possible to preserve teeth even in the presence of gum disease. By practicing good oral hygiene habits, such as regular brushing and flossing, and visiting the dentist for check-ups and cleanings, individuals can effectively manage and slow down the progression of periodontal disease.
It is important to recognize the risk factors associated with periodontal disease, such as smoking, poor oral hygiene, and certain systemic health conditions. By managing these risk factors and seeking timely dental treatment, individuals can significantly reduce the likelihood of tooth loss.
Preserving teeth with gum disease requires a proactive approach to dental care. By adopting a healthy diet, avoiding tobacco products, and maintaining overall good health, individuals can support their oral health and safeguard their teeth.
In conclusion, while periodontal disease poses a risk to tooth retention, it is not a guarantee of tooth loss. With a commitment to oral care and regular dental visits, individuals with gum disease can successfully preserve their teeth for a lifetime. Remember, your dental health is within your control, and by taking proper care of your teeth, you can maintain a confident smile and ensure your overall dental well-being.
FAQ
How long can you keep your teeth with periodontal disease?
With proper oral care and management, it is possible to maintain teeth even with periodontal disease.
What are the symptoms of periodontal disease?
Symptoms of periodontal disease include persistent bad breath, redness and swelling in the gums, tooth sensitivity, bleeding gums, tender gums, gum redness, gum recession, and tooth loss.
How long can teeth last with periodontal disease?
Studies have shown that with proper oral care, approximately 50% of patients with periodontal disease experience tooth loss over a 12-year period. However, with effective management and treatment, it is possible to preserve teeth even with periodontal disease.
What are the risk factors for periodontal disease?
Risk factors for periodontal disease include stress, smoking or chewing tobacco, poor oral hygiene, systemic diseases such as diabetes, malnutrition, pregnancy, cancer therapy, medication, obesity, and certain medical conditions like Alzheimer’s disease.
How can you reverse periodontal disease?
Treatment options for periodontal disease include scaling and root planing, gum grafts, bone grafting, and maintaining good oral hygiene practices. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are also essential.
How can I maintain dental health with periodontal disease?
Maintaining dental health with periodontal disease involves practicing good oral hygiene, including brushing twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush and flossing daily. Regular dental check-ups and cleanings are also important.
What is the link between periodontal disease and overall health?
Research has shown associations between periodontal disease and conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, respiratory disease, and certain types of cancer. By preventing and treating periodontal disease, overall health can be improved.
What is the conclusion regarding preserving teeth with gum disease?
By following proper oral care practices, managing risk factors, and seeking timely dental treatment, individuals with periodontal disease can keep their teeth for a lifetime. Regular dental check-ups, cleanings, and professional advice are essential for preserving teeth and overall dental health.