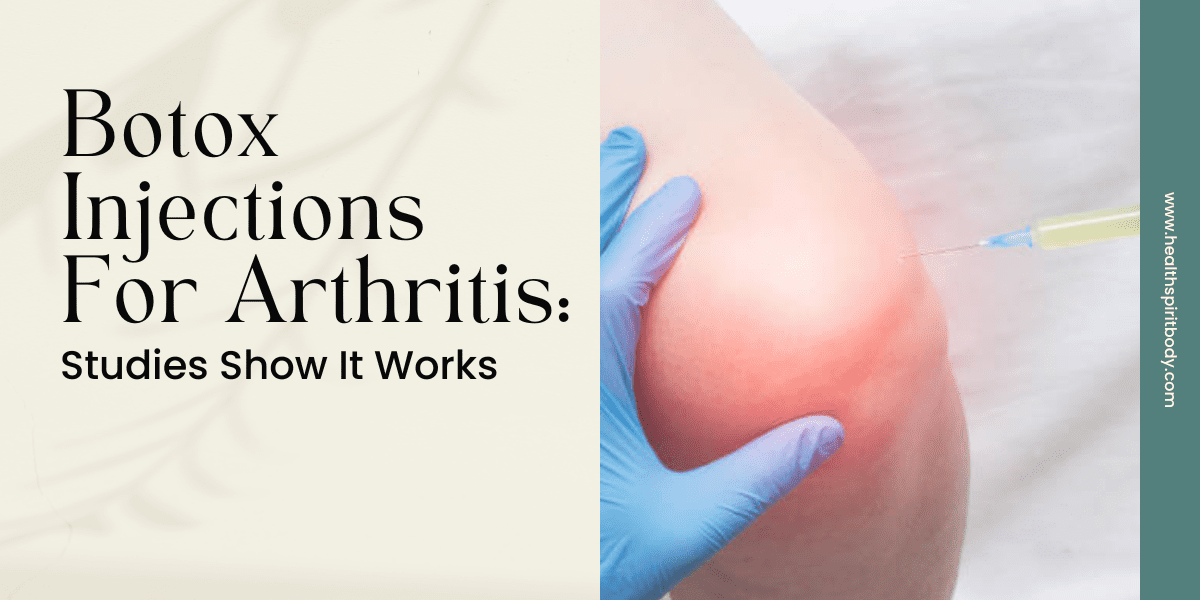
Osteoarthritis is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Osteoarthritis is a condition that causes the joints to break down. This can lead to pain, stiffness, and swelling. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and can make everyday activities quite difficult. There is no cure for osteoarthritis, but there are treatments available that can help relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. One such treatment is botox injections.
Botox is most commonly associated with cosmetic procedures like reducing wrinkles or forehead creases. However, botox can also be used to treat various medical conditions, including migraines, excessive sweating, and muscle spasms. In recent years, botox has also been shown to be an effective treatment for osteoarthritis.
You may have heard of Botox being used for cosmetic purposes, but did you know that it can also help with osteoarthritis? Botox is a form of botulinum toxin, which is a protein that helps to relax the muscles. When injected into the muscles, it can help to reduce the appearance of wrinkles. But how does it help with osteoarthritis?
How Does Botox Help Osteoarthritis?
There are many different ways in which botox can help relieve osteoarthritis symptoms. For one, botox injections can help reduce inflammation in the joints. This can lead to reduced pain and stiffness and improved joint function. Additionally, botox can help reduce muscle spasms around the joints. This can further improve joint function and reduce pain.
Another way in which botox can help people with osteoarthritis is by decreasing the production of certain chemicals that are associated with pain signals. By reducing the level of these chemicals in the body, pain signals are less likely to reach the brain, leading to reduced pain overall.
Are There Any Side Effects?
It’s important to know that there are some potential side effects associated with botox for osteoarthritis. These can include muscle weakness, joint stiffness, and fatigue. In rare cases, botulism poisoning has been reported. This is why it’s important to talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of this treatment option before deciding if it’s right for you.
Finally, keep in mind that botox injections are not a cure for osteoarthritis. They are only meant to provide temporary relief from symptoms. If you’re considering this treatment option, be sure to discuss all of your expectations with your doctor so that you can make an informed decision.

Are Botox Injections Effective For Treating Arthritis?
The short answer is yes, botox injections can be effective for treating arthritis. In a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, patients who received botox injections reported a significant reduction in pain compared to those who did not receive any treatment at all. Botox works by paralyzing the muscles around the affected joints, which helps to reduce inflammation and pain.
However, it’s important to keep in mind that botox is not a cure for arthritis. The effects of the injections only last for a few months, so patients will need to continue receiving treatments on a regular basis in order to maintain relief from their symptoms. Additionally, botox injections are not appropriate for everyone; some people may experience side effects such as bruising or muscle weakness.
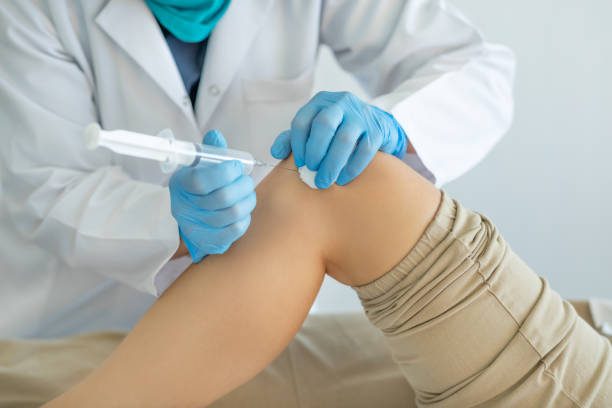
How Much Do Botox Injections For Arthritis Cost?
There is no set cost for botox injections, as the price will vary depending on the clinic or doctor you see. However, you can expect to pay anywhere from $200 to $1,000 per treatment. Most insurance plans do not cover the cost of botox injections for cosmetic purposes, but some may cover the cost if the injections are being used for medical reasons.

If you’re considering botox injections for the treatment of arthritis, be sure to consult with a qualified doctor or healthcare provider to see if they are right for you.
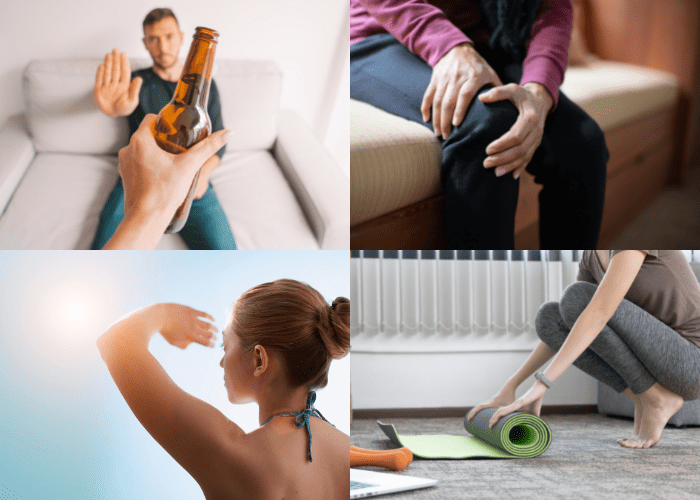
What To Avoid Following An Arthritis Botox Injection
After receiving a botox injection, it’s important to avoid certain activities in order to reduce the risk of side effects. These include:
• Avoid strenuous activity or exercise for at least 24 hours after the injection.
• Avoid touching or rubbing the injection site.
• Avoid exposure to sunlight or heat for at least 24 hours after the injection.
• Avoid alcohol for at least 24 hours after the injection.

Final Thoughts
Botox injections can be an effective treatment for osteoarthritis, providing relief from pain, inflammation, and muscle spasms. However, it’s important to keep in mind that botox is not a cure for arthritis, and the effects of the injections only last for a few months. Additionally, botox injections are not appropriate for everyone, and some people may experience side effects. If you’re considering this treatment option, be sure to consult with a qualified healthcare provider to see if it’s right for you.
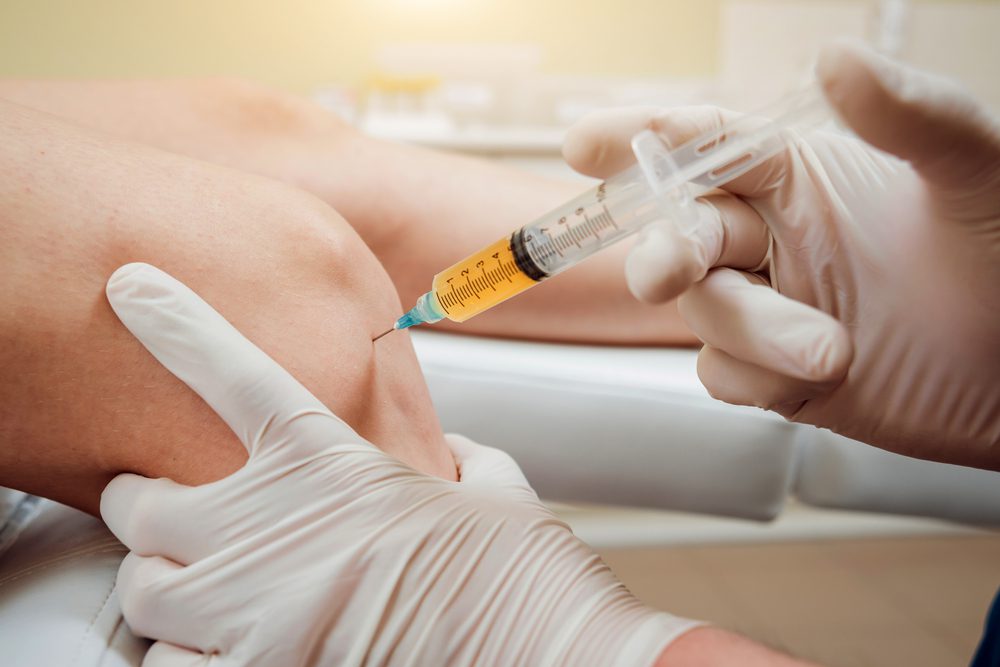
Frequently Asked Questions:
Who should not get Botox?
You might not be a suitable candidate for Botox if your general health is poor, your skin is excessively thick, or you already have a muscular weakness where the injection is planned. In addition, an allergic reaction at the injection site is possible in patients with sensitive skin.
Are there any adverse long-term effects of Botox?
The use of botulinum toxin for any aesthetic indication does not have any long-term or fatal side effects. Furthermore, the risk of potential problems can be decreased by carefully examining the patient's medical history and using the right dosage and method for the injection.
Do any medications interfere with Botox?
Certain antibiotics (including aminoglycosides like gentamicin and polymyxin), anticoagulants (such as warfarin), medications for Alzheimer's disease (such as galantamine, rivastigmine, and tacrine), medications for myasthenia gravis (such as ambenonium, pyridostigmine), and quinidine are a few examples of products that may interact with this medication.
What happens after years of Botox use?
Repeated Botox injections into the same place of the body over time may also result in the muscle's permanent paralysis. One of the most significant and harmful adverse effects of receiving Botox injections is, by far, this. Toxins have the potential to infiltrate into nearby tissues, which can be lethal.
How long does Botox for pain take to work?
In order to stop the nerves from contracting muscles, botulinum toxin binds to the junction between muscles and nerves. After that, the muscle begins to relax, which reduces its sensitivity to nerve stimulation and resting tone. Typically, two to four weeks following the injection, this effect appears.




